Prevalence, risk factors, microbiological results and clinical outcome in unexpected positive intraoperative cultures in unclear and presumed aseptic hip and knee revision arthroplasties - A ten-year retrospective analysis with a minimum follow up of 2 years
- PMID: 39247790
- PMCID: PMC11380463
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.08.002
Prevalence, risk factors, microbiological results and clinical outcome in unexpected positive intraoperative cultures in unclear and presumed aseptic hip and knee revision arthroplasties - A ten-year retrospective analysis with a minimum follow up of 2 years
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to assess the prevalence, microbiological spectrum, risk factors, and clinical outcomes of unexpected-positive-intraoperative-cultures (UPIC) in presumed aseptic and unclear revision-total-hip-/knee-arthroplasties (rTHA and rTKA) compared to culture-negative (CN) revisions.
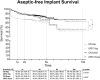
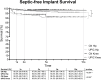
Methods: This study reviewed all International-consensus-meeting-2018 (ICM 2018) negative or inconclusive rTHA (n = 751) and rTKA (n = 679) performed at our institution from 2011 to 2020 with a minimum follow-up of two years. A Kaplan-Meier-analysis was performed to determine the septic and aseptic-free implant survival in cases with UPIC's and matched culture-negative cases. Patient demographics, risk factors, microbiological spectrum and clinical outcomes were evaluated.
Results: There were significantly more UPIC cases in rTHA 196/751 (26.1 %) compared to rTKA 113/679 (16.6 %); (p < 0.001). UPICs in rTKA and rTHA have a lower septic and aseptic implant-free-survival compared to CN revisions. Patients with a history of nickel allergy have a higher risk of an UPIC in rTHA and rTKA (p < 0.001). Septic re-revisions after UPIC had a significantly (H: p = 0.004; K: p = 0.030) shorter time period to the primary/previous surgery (H: 84 (IQR:41-797); K: 115 (IQR:55-446)) compared to patients with aseptic re-revisions after UPIC (H:1248 (IQR:178-3534); K: 827 (IQR:361-1183)).
Conclusion: UPICs have a higher rate of septic and aseptic failure than CN outcomes. UPICs are twice as common in rTHA compared to rTKA. Preoperative PJI workup reduces the UPIC rate. Nickel allergy is a risk factor for UPIC. Early revisions with UPICs after primary THA or TKA have a higher risk of septic failure.
The translational potential of this article: This article provides new information on revision rates for UPIC and potential risk factors for UPIC and its treatment failure.
Keywords: Aseptic implant-free survival; Revision-total-hip-arthroplasty; Revision-total-knee-arthroplasty; Risk factors; Septic and unexpected-positive-intraoperative-cultures.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alpha-defensin as a diagnostic tool in revision total knee arthroplasties with unexpected positive intraoperative cultures and unexpected culture negative intraoperative cultures.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023 Apr;31(4):1462-1469. doi: 10.1007/s00167-022-07268-w. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023. PMID: 36509937
-
Prevalence, interpretation, and management of unexpected positive cultures in revision TKA: a systematic review.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Dec;30(12):3998-4009. doi: 10.1007/s00167-021-06856-6. Epub 2022 Jan 15. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022. PMID: 35031821 Review.
-
The unsuspected prosthetic joint infection : incidence and consequences of positive intra-operative cultures in presumed aseptic knee and hip revisions.Bone Joint J. 2017 Nov;99-B(11):1482-1489. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.99B11.BJJ-2016-0655.R2. Bone Joint J. 2017. PMID: 29092987
-
Unexpected low-grade infections in revision hip arthroplasty for aseptic loosening : a single-institution experience of 274 hips.Bone Joint J. 2021 Jun;103-B(6):1070-1077. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.103B6.BJJ-2020-2002.R1. Bone Joint J. 2021. PMID: 34058865
-
Unexpected positive intraoperative cultures (UPIC) in revision Hip and knee arthroplasty- A review of the literature.J Orthop. 2019 Jul 2;17:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2019.06.028. eCollection 2020 Jan-Feb. J Orthop. 2019. PMID: 31879464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Septic Hip Revision Arthroplasty-A Perioperative and Follow-Up Risk Analysis.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 18;13(20):6202. doi: 10.3390/jcm13206202. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39458152 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

